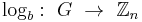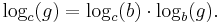Discrete logarithm
In mathematics, specifically in abstract algebra and its applications, discrete logarithms are group-theoretic analogues of ordinary logarithms. In particular, an ordinary logarithm loga(b) is a solution of the equation ax = b over the real or complex numbers. Similarly, if g and h are elements of a finite cyclic group G then a solution x of the equation gx = h is called a discrete logarithm to the base g of h in the group G.
Contents |
Example
Discrete logarithms are perhaps simplest to understand in the group (Zp)×. This is the set {1, …, p − 1} of congruence classes under multiplication modulo the prime p.
If we want to find the kth power of one of the numbers in this group, we can do so by finding its kth power as an integer and then finding the remainder after division by p. This process is called discrete exponentiation. For example, consider (Z17)×. To compute 34 in this group, we first compute 34 = 81, and then we divide 81 by 17, obtaining a remainder of 13. Thus 34 = 13 in the group (Z17)×.
Discrete logarithm is just the inverse operation. For example, take the equation 3k ≡ 13 (mod 17) for k. As shown above k=4 is a solution, but it is not the only solution. Since 316 ≡ 1 (mod 17) it also follows that if n is an integer then 34+16 n ≡ 13 × 1n ≡ 13 (mod 17). Hence the equation has infinitely many solutions of the form 4 + 16n. Moreover, since 16 is the smallest positive integer m satisfying 3m ≡ 1 (mod 17), i.e. 16 is the order of 3 in (Z17)×, these are the only solutions. Equivalently, the solution can be expressed as k ≡ 4 (mod 16).
Definition
In general, let G be a finite cyclic group with n elements. We assume that the group is written multiplicatively. Let b be a generator of G; then every element g of G can be written in the form g = bk for some integer k. Furthermore, any two such integers k1 and k2 representing g will be congruent modulo n. We can thus define a function
(where Zn denotes the ring of integers modulo n) by assigning to each g the congruence class of k modulo n. This function is a group isomorphism, called the discrete logarithm to base b.
The familiar base change formula for ordinary logarithms remains valid: If c is another generator of G, then we have
Algorithms
| Can the discrete logarithm be computed in polynomial time on a classical computer? |
No efficient classical algorithm for computing general discrete logarithms logb g is known. The naive algorithm is to raise b to higher and higher powers k until the desired g is found; this is sometimes called trial multiplication. This algorithm requires running time linear in the size of the group G and thus exponential in the number of digits in the size of the group. There exists an efficient quantum algorithm due to Peter Shor.[1]
More sophisticated algorithms exist, usually inspired by similar algorithms for integer factorization. These algorithms run faster than the naive algorithm, but none of them runs in polynomial time (in the number of digits in the size of the group).
- Baby-step giant-step
- Pollard's rho algorithm for logarithms
- Pollard's kangaroo algorithm (aka Pollard's lambda algorithm)
- Pohlig–Hellman algorithm
- Index calculus algorithm
- Number field sieve
- Function field sieve
Comparison with integer factorization
While the problem of computing discrete logarithms and the problem of integer factorization are distinct problems they share some properties:
- both problems are difficult (no efficient algorithms are known for non-quantum computers),
- for both problems efficient algorithms on quantum computers are known,
- algorithms from one problem are often adapted to the other, and
- the difficulty of both problems has been utilized to construct various cryptographic systems.
Cryptography
There exist groups for which computing discrete logarithms is apparently difficult. In some cases (e.g. large prime order subgroups of groups (Zp)×) there is not only no efficient algorithm known for the worst case, but the average-case complexity can be shown to be about as hard as the worst case using random self-reducibility.
At the same time, the inverse problem of discrete exponentiation is not difficult (it can be computed efficiently using exponentiation by squaring, for example). This asymmetry is analogous to the one between integer factorization and integer multiplication. Both asymmetries have been exploited in the construction of cryptographic systems.
Popular choices for the group G in discrete logarithm cryptography are the cyclic groups (Zp)×; see ElGamal encryption, Diffie–Hellman key exchange, and the Digital Signature Algorithm.
Newer cryptography applications use discrete logarithms in cyclic subgroups of elliptic curves over finite fields; see elliptic curve cryptography.
References
- ^ Shor, Peter (1997). "Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum Computer". SIAM Journal on Computing 26 (5): 1484–1509. arXiv:quant-ph/9508027.
- Richard Crandall; Carl Pomerance. Chapter 5, Prime Numbers: A computational perspective, 2nd ed., Springer.
- Stinson, Douglas Robert (2006), Cryptography: Theory and Practice (3rd ed.), London: CRC Press, ISBN 978-1-58488-508-5
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||